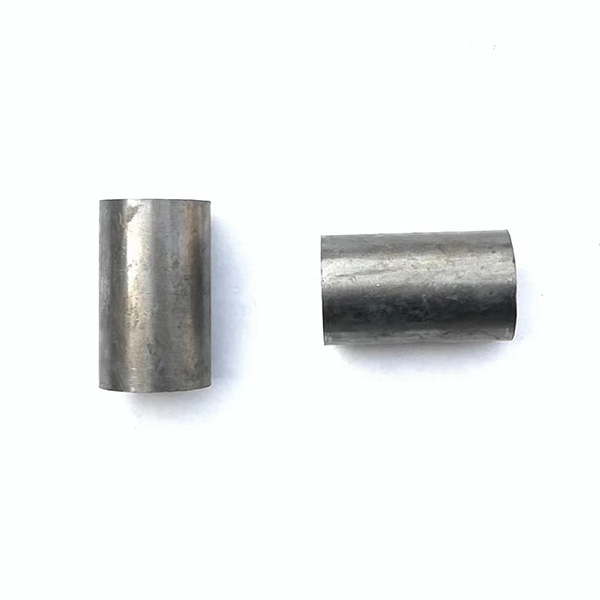
Sleeve
Sleeves are crucial components in many systems and applications,offering protection,support,and functionality across a wide range of industries.
A sleeve is a cylindrical or tubular component used in various industries for protection, support, or as a functional interface. It is designed to fit over or around another component, offering benefits such as wear resistance, alignment, or insulation. Sleeves come in different materials and configurations, depending on their specific purpose, and are widely used in automotive, construction, machinery, and electronics sectors.
Key Features:
Material:
Metal Sleeves:
Made from materials like steel, aluminum, or brass.
Provide structural support and wear resistance.
Plastic Sleeves:
Constructed from polymers such as nylon, PVC, or PTFE.
Offer insulation and chemical resistance in various applications.
Rubber Sleeves:
Composed of natural or synthetic rubbers.
Used for cushioning, vibration dampening, and flexibility.
Design:
Cylindrical Shape: The most common design, used to fit around pipes, rods, or wires.
Custom Shapes: Tailored sleeves are sometimes manufactured with specific contours to suit unique applications.
Dimensions: Sleeves come in various diameters, lengths, and wall thicknesses to meet different operational requirements.
Finish: Surface finishes may vary, such as smooth, textured, or coated, depending on application needs.
Applications:
Automotive:
Protective covers for wires, cables, and hydraulic lines to prevent abrasion and damage.
Construction:
Used as liners or protective barriers for pipes and rods, preventing corrosion and wear.
Industrial Machinery:
In bearings, shafts, and other moving parts to reduce friction and extend component life.
Electronics:
Acts as insulation for electrical wires to prevent short circuits and ensure safety.
Advantages:
Protection: Shields components from wear, corrosion, and environmental factors.
Support: Adds structural reinforcement or provides alignment for components.
Insulation: Provides electrical or thermal insulation, depending on the material.
Ease of Installation: Designed for easy fitting over or around components, simplifying the assembly process.
Types of Sleeves:
Bearing Sleeves:
Used to minimize friction and wear between rotating or sliding components in machinery.
Cable Sleeves:
Provide insulation and protection for electrical cables from damage.
Pipe Sleeves:
Protect pipes from external damage, corrosion, or thermal stress.
Hydraulic Sleeves:
Cover hydraulic lines and hoses, preventing abrasion and leaks.
Safety Considerations:
Ensure the sleeve material and design meet the operating requirements for temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure.
Regularly inspect sleeves for wear, damage, or deterioration to maintain safety and performance.
Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper installation and use to ensure optimal performance.