Introduction to Parking Heaters
Parking heaters are essential for maintaining vehicle comfort and engine performance during cold weather. They allow drivers topreheat the cabin and engine without running the main engine, reducing wear and improving fuel efficiency. When selecting a parking heater, understandingpower consumption and operating costs is crucial. The two primary types areelectric heaters andfuel-powered heaters, each with distinct cost implications.
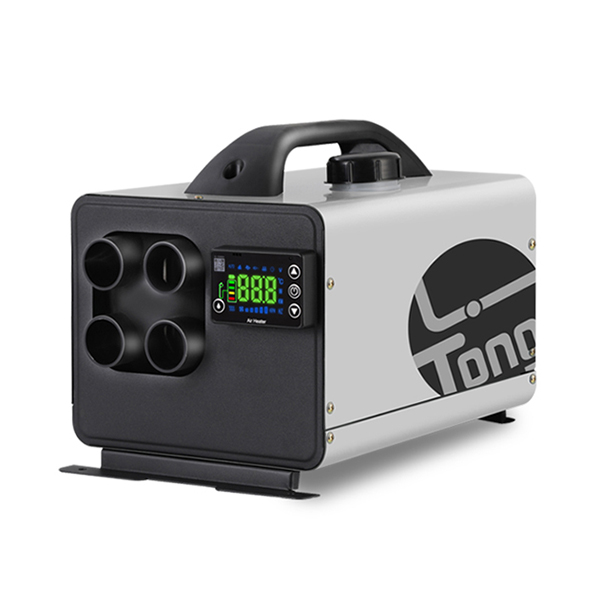
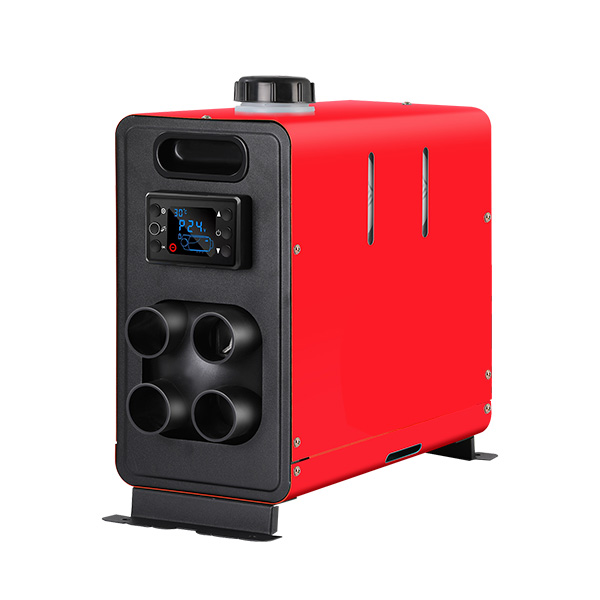


Electric Parking Heaters: Power Usage and Costs
Electric parking heaters draw energy directly from the vehicle’s battery or an external power source. They are known forclean operation and minimal emissions.
Key characteristics of electric heaters:
1. Power Consumption: Typically rated between 1–3 kW. Operating cost depends on electricity rates and heater efficiency.
2. Silent Operation: Electric heaters run quietly, providing a comfortable cabin environment.
3. Zero Fuel Use: No direct fuel consumption, reducing engine wear.
4. Fast Heating: Ideal for short preheating periods in mild to moderate cold conditions.
Cost Analysis:
The electricity cost can be calculated using the formula:
Cost = Power (kW) × Usage Time (hours) × Electricity Rate ($/kWh)
For example, a 2 kW electric heater running for 3 hours at $0.15/kWh would cost:
2 × 3 × 0.15 =$0.90 per session
Electric heaters are convenient and environmentally friendly but may be limited in extremely cold climates due to battery capacity.
Fuel-Powered Parking Heaters: Consumption and Costs
Fuel-powered parking heaters operate using diesel or gasoline drawn from the vehicle’s fuel tank. These heaters are popular in heavy-duty vehicles and regions with very low temperatures.
Key characteristics of fuel-powered heaters:
1. Fuel Consumption: Typically between 0.1–0.5 liters per hour, depending on heater size and operating conditions.
2. High Heat Output: Effective for prolonged heating and very cold environments.
3. Independent of Battery: Can run without draining the vehicle’s battery.
4. Durability: Designed for heavy-duty use and long-term operation.
Cost Analysis:
Fuel cost can be calculated as:
Cost = Fuel Consumption (liters/hour) × Usage Time (hours) × Fuel Price ($/liter)
For example, a heater consuming 0.3 L/h of diesel at $1.20/L for 3 hours:
0.3 × 3 × 1.20 =$1.08 per session
While fuel-powered heaters have higher operating costs than electric heaters in some regions, they provide greater heat output and reliability in extreme cold.
Comparison: Electric vs Fuel-Powered Parking Heaters
Feature | Electric Heater | Fuel-Powered Heater |
Operating Cost | Lower in regions with cheap electricity | Higher due to fuel cost |
Heat Output | Moderate, suitable for short preheating | High, ideal for prolonged or extreme cold |
Environmental Impact | No direct emissions | Emits CO2 and particulates |
Battery Dependence | Requires battery or external power | Independent of battery |
Installation & Maintenance | Simple, low maintenance | Requires fuel line, higher maintenance |
Choosing the right heater depends on climate, vehicle type, usage duration, and energy cost considerations.
Tips to Reduce Parking Heater Costs
1. Optimize Preheating Time: Avoid running heaters longer than necessary.
2. Insulate the Cabin: Reduce heat loss to improve efficiency.
3. Monitor Electricity or Fuel Rates: Schedule heating when energy costs are lower if possible.
4. Regular Maintenance: Clean filters and check connections to ensure efficient operation.
5. Use Timers or Smart Controls: Automate heating for optimal power usage without waste.
Conclusion: Balancing Efficiency and Comfort
Electric and fuel-powered parking heaters each offer unique benefits and cost structures. Electric heaters areeconomical, quiet, and eco-friendly, ideal for moderate climates or short preheating sessions. Fuel-powered heaters providehigh heat output and reliability for long-term operation in extreme cold but with higher fuel costs. Understanding power consumption, fuel usage, and operating conditions helps vehicle owners make informed decisions, balancing comfort, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Meta Description:
Compare electric vs fuel-powered parking heaters for cost, efficiency, and performance. Learn how power consumption affects operating expenses and discover tips to optimize heater usage.